Regenerative braking
Regenerative braking is a critical feature of modern EVs, allowing the vehicle to recover energy during braking and deceleration.
Last modified: Feb 02, 2026By converting the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy and storing it in the battery, regenerative braking can extend the vehicle’s range and improve overall efficiency. This article explores the different types of regenerative braking strategies used in EVs, their benefits, and their limitations.
How does it work?
Regenerative braking captures the kinetic energy of a moving vehicle and stores it as electrical energy in the vehicle’s battery during braking or deceleration.
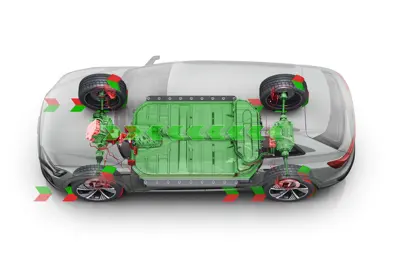
An electric motor can function as a generator in an EV by using the principle of electromagnetic induction, which states that a change in the magnetic field around a conductor generates an electric current in the circuit. When an electric motor rotates, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the stator windings and produces an electric current that powers the vehicle. When the car decelerates or brakes, the wheels drive the motor in reverse, causing the magnetic field to change direction and induce electric current in the opposite direction. This current can be fed back to the battery and stored as energy, reducing the need for conventional friction brakes and increasing the range and efficiency of the EV.
Types of Regenerative Braking Strategies
EV manufacturers provide regenerative braking with different strategies. There are three main types of regenerative braking strategies. Some manufacturers offer only one option, while others let the driver choose between two or all three.
One-Pedal Driving / Lift-Off Regen
One-pedal driving is a feature of some electric vehicles that allows the driver to control the acceleration and deceleration of the car using only the accelerator pedal.
When the driver presses the pedal, the vehicle accelerates. When the driver releases the pedal, the car decelerates using regenerative braking, which converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy that the EV stores in the battery. This type of regenerative braking is also called throttle lift-off regen. Depending on the vehicle settings and driving conditions, one-pedal driving can bring the vehicle to a complete stop or maintain a low speed until the driver presses the pedal again.
The benefit of one-pedal driving is that it simplifies driving by requiring only one pedal.
The cons of one-pedal driving are that it can require some adaptation from drivers used to traditional two-pedal driving. Full lift-off regen can be a disadvantage on slippery roads since it will brake hard if you quickly remove your foot from the pedal. Many recommend reducing the regenerative force in winter.
We recomend watching this video from Out of Spec showing how lift-up regen can affect the stability on slippery surface.
Additionally, its performance can vary depending on factors such as battery state of charge, temperature, road gradient, and traffic flow. While some EVs have a fixed level of regen for one-pedal driving, others have paddles on the steering wheel to activate regen at different levels.
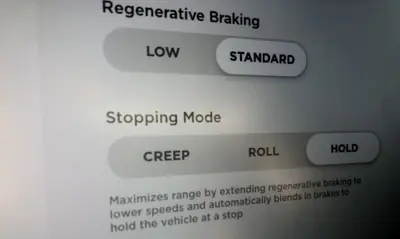
Others, like Tesla, have settings available in their infotainment system.
In the picture above, you also see how Tesla lets the driver decide how the car should behave at low speed. For example, they can add physical brakes at low vehicle speeds to make the vehicle entirely stop and hold.
Manual Regen Using the Brake Pedal
By pressing the brake pedal, you can regenerate energy on EVs with blended brakes.
Regen using a blended brake system in EVs uses sensors and algorithms to determine the optimal balance between regenerative braking and friction braking, depending on factors such as driver input, battery state of charge, road conditions, traffic situation, and vehicle speed.
The system can also work with driver assistance systems such as adaptive cruise control or collision avoidance to enhance safety and convenience.
Adaptive Regen
Adaptive regen is a feature of some electric vehicles that allows them to adjust the level of regenerative braking according to the driving situation.
Adaptive regen works by using sensors, cameras, and navigation data to detect traffic conditions, road curvature, speed limits, and other factors that affect the optimal deceleration rate of the vehicle. Based on this information, the system can automatically increase or decrease the regen level when the driver releases the accelerator pedal without requiring manual input or mode selection.
The benefit of adaptive regen is that it can provide a smoother and more natural driving experience and more effective energy recovery. By adjusting the regen level according to the situation, adaptive regen can avoid excessive or insufficient braking that might cause discomfort or waste energy since it will coast when possible. The adaptive regen can also work with driver assistance systems to enhance safety and convenience, such as maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle ahead or slowing down for a sharp turn.
Some examples of EVs that offer adaptive regen are the Porsche Taycan and the BMW i4. These EVs use different technologies and algorithms to implement adaptive regen, but all aim to provide their drivers with a better one-pedal driving experience.
Max Regenerative Braking Power
The maximum regenerative power of an EV depends on several factors, such as the type and size of the motor, the speed and state of charge of the battery, and the settings and modes of the vehicle. Different EVs have different levels of regenerative braking, but typically, it ranges from above 50kW on small cars to 300kW on the most powerful.
Brake Lights & Regenerative Braking
Typical brake lights will come on as long as the braking force is high enough to reduce speed substantially. But this is not always the case. For example, the Hyundai Ioniq 5 does not enable the brake lights when using one-pedal driving. This behavior can be dangerous. This danger is explained in this video. Check how your EV works so you are not rear-ended. In Europe, the regulation is that if deceleration is above 1.3 m/s², it should generate a brake signal.
Benefits of Regenerative Braking
There are several benefits to regenerative braking, including:
Improved Efficiency: By recovering energy during braking and deceleration, regenerative braking can extend the vehicle’s range and improve efficiency.
Reduced Wear on Brakes: Because regenerative braking can handle much of the vehicle’s braking force, it can reduce wear on its mechanical brakes, leading to lower maintenance costs.
Smoother Braking: Regenerative braking can provide smoother and more consistent braking than traditional friction brakes, leading to a more comfortable ride for passengers.
Limitations of Regenerative Braking
While regenerative braking offers many benefits, the technology has some limitations. These include:
Reduced Effectiveness at High Speeds: Regenerative braking is less effective at high speeds, as the amount of kinetic energy that can be captured and stored decreases as the vehicle's speed increases.
Limited Range Extension: Regenerative braking can extend the vehicle’s range, but the amount of energy the car recovers is limited, and the overall impact on the vehicle range can vary depending on driving conditions.
Reduced Brake Feel: Because regenerative braking uses the electric motor to slow the vehicle, it can reduce the brake pedal's feel, making it less intuitive for some drivers.
How Much Can Be Regenerated?
In the second part, we provide detailed calculations on how much energy can be regenerated and how that affects range. We also explain the physics behind the math.