Battery Pack & Configuration
The battery system combines many cells and other control electronics into a full battery to power the EV.
Last modified: Dec 31, 2024Battery Configuration
In an electric vehicle (EV), the battery configuration refers to the arrangement of individual battery cells within the battery pack. This configuration affects the voltage, capacity, power output, and overall vehicle performance.
The most common configuration for EV batteries is a series-parallel hybrid. In this setup, multiple cells are connected in series to increase the battery pack's voltage, and multiple groups of series-connected cells are then connected in parallel to increase the battery pack's overall capacity.
- Series Connection: Increases the battery pack’s voltage, which is vital for providing the necessary power to drive the vehicle.
- Parallel Connection: Increases the battery pack’s capacity, essential for storing the energy required to achieve the desired range.
To calculate the gross battery pack size, multiply the total parallel capacity in ampere-hours (Ah) by the battery pack's nominal voltage in volts (V). The result is in watt-hours (Wh).
Example: Audi Q8 e-tron 55
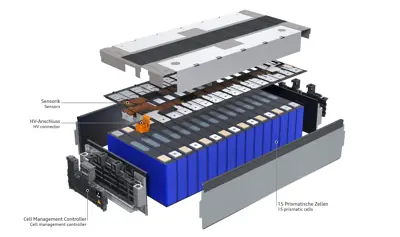
The diagram below shows the configuration of a battery module from the Audi Q8 e-tron 55. This module contains 12 battery cells, four of which are mounted in parallel, and there are three groups of this parallel configuration in series.

3s4p Module
- Cell Specifications: Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3.6667 volts and a capacity of 72 Ah.
- Module Voltage: Three cells in series give a module voltage of 11 volts.
- Module Capacity: 4 x 72 Ah in parallel gives a total module capacity of 288 Ah.
- Pack Voltage: The Q8 e-tron 55 has a total of 36 modules in series. 36 x 11 volts gives 396 volts for the pack.
- Gross Capacity: 396 volts x 288 Ah = 114,048 Wh or 114 kWh gross capacity.
Example: Tesla Model Y Long Range
The Tesla Model Y Long Range uses 4,416 cells in the small 21700 format, with 96 rows and 46 cells in parallel.
- Cell Specifications: Each cell is 4.8 Ah with a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts.
- Parallel Capacity: 4.8 Ah x 46 gives a total of 220.8 Ah.
- Pack Voltage: 96 x 3.7 volts gives a nominal pack voltage of 355 volts.
- Gross Capacity: 355 volts x 220.8 Ah = 78.4 kWh.
Example: Kia EV6 Long Range
The Kia EV6 long-range battery has 384 cells in total, configured in 192 rows with two cells in parallel, structured in modules with 12 cells.

6s2p Module
- Cell Specifications: Each cell is 55.6 Ah.
- Parallel Capacity: 2 x 55.6 Ah = 111.2 Ah.
- Pack Voltage: The nominal voltage is 3.63 volts per cell. 192 x 3.63 volts = 696.96 volts nominal for the pack.
- Gross Capacity: 696.96 volts x 111.2 Ah = 77.5 kWh.
More Battery Pack Examples
Here are some configuration examples:
| Model | Gross Capacity | Configuration | Nominal Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audi Q8 e-tron | 116 kWh | 108s4p | 396 volts |
| Audi e-tron GT | 93.7 kWh | 198s2p | 725 volts |
| Kia EV6 GT | 77.4 kWh | 192s2p | 697 volts |
| Nio 100 kWh Battery | 100 kWh | 96s1p | 358 volts |
| Mercedes EQE | 96.12 kWh | 90s4p | 328 volts |
| Mercedes EQS | 120 kWh | 108s4p | 396 volts |
| Tesla Model Y Long Range | 78.1 kWh | 96s46p | 357 volts |
| Rivian R1S Large Pack | 135 kWh | 108s72p | 390 volts |
| Rivian R1S Max Pack | 149 kWh | 108s72p | 390 volts |
| Porsche Macan / Audi Q6 | 100 kWh | 180s1p | 662 volts |
The specific battery configuration used in an EV depends on various factors, such as the desired range, power output, and overall vehicle weight.
400 or 800 Volts?
Manufacturers typically configure battery packs to be around 400 volts or 800 volts. Each configuration has its pros and cons:
Pros of 400 Volt Package
- More Mature Technology: 400-volt systems are more proven and reliable.
- Lower Cost: Less expensive to produce.
- Widely Available Charging Infrastructure: Easier to find charging stations.
- More Available Cell Configurations: Offers more flexibility in cell options.
Cons of 400 Volt Package
- Slower Charging: Requires longer charging times.
- Limited Power Output: May not deliver the same power as 800-volt systems.
- Heavier: Requires thicker cables for the same charging speed.
Pros of 800 Volt Package
- Faster Charging: Supports higher charging speeds.
- Higher Power Output: Can deliver more power.
- Lighter Weight: Requires thinner cables.
Cons of 800 Volt Package
- Limited Charging Infrastructure: Fewer public charging stations support 800-volt charging.
- Requires Smaller Cells: Prevents the use of larger cells, which offer higher density and less wiring.
Battery Pack Designs
There are several standard designs used to build battery packs.
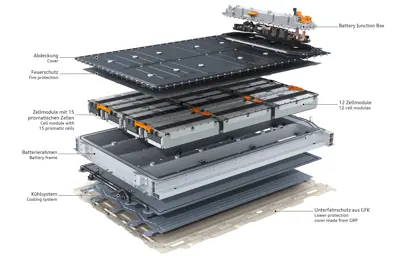
Cell-to-Module (C2M)
The Cell-to-Module (C2M) design involves assembling multiple battery cells into a single, self-contained module with integrated electronics and cooling systems. These modules can then be easily connected to form the complete battery pack.
Each module has its own Battery Management System (BMS) that monitors and controls the charging and discharging of the cells within the module, allowing for more precise control and monitoring of individual cells.
Advantages of Cell-to-Module (C2M):
- Modularity: Individual battery modules can be replaced or serviced independently. If a module fails, it can be swapped out without affecting the entire battery pack.
- Thermal Management: Modules provide space for thermal management components (such as cooling plates or liquid cooling channels), helping to regulate cell temperature and ensure optimal performance.
- Scalability: C2M designs allow flexibility in configuring battery packs. Manufacturers can adjust the number of modules to meet different vehicle requirements (e.g., range, power, or size).
- Safety: Isolating cells within modules enhances safety. If a cell experiences thermal runaway or other issues, it won’t directly impact neighboring cells.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Building modules separately simplifies assembly and quality control. It also enables parallel production of modules, streamlining the manufacturing process.
Cell-to-Pack (CTP)
Cell-to-Pack (CTP) batteries are a new type of battery technology that eliminates the need for battery modules by integrating the cells directly into the pack. Several companies, such as Tesla, BYD, and CATL, are developing this technology.
BYD Blade and CATL Qilin are two examples of CTP batteries. The main difference between these two batteries is their cooling system. BYD Blade uses a liquid cooling system, while CATL Qilin uses a structural cooling system, which is more efficient.
Advantages of Cell-to-Pack (CTP):
- Simplicity: CTP designs eliminate the need for intermediate modules, reducing complexity. The battery pack directly integrates individual cells.
- Space Utilization: Without modules, more space is available for cells, potentially increasing energy density.
- Cost Efficiency: Fewer components (no modules) can lead to cost savings in production and assembly.
- Weight Reduction: Eliminating module casings reduces overall weight, improving vehicle efficiency.
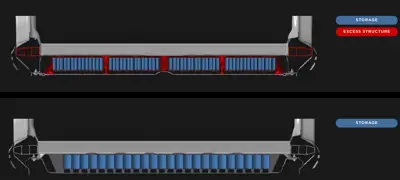
Structural Battery Pack
A structural battery pack is designed to become a structural component of the EV. This approach can reduce the EV’s weight by removing duplicate structures between the pack and the vehicle structure, as the battery pack becomes part of the vehicle structure.
This design can improve the EV’s overall performance and efficiency. Structural battery packs are still relatively new, but several companies and research institutions are exploring and developing them.
Structural battery packs, a game-changer in EV design, offer many benefits. They trim weight and complexity, boost performance, and facilitate seamless integration of battery technology across various applications.
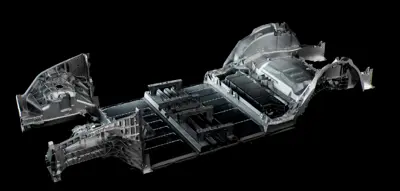
Tesla Model Y and Tesla Cybertruck are two models that have structural packs. According to Tesla, this solution presents many advantages, such as significantly reducing the number of parts used in both the battery pack and the car.
More importantly, the company said the new cells and the structural pack are expected to increase the Model Y's range by 16 percent and decrease the car's overall weight by 10 percent, resulting in improved acceleration and handling.
Tesla uses pink polyurethane foam to encapsulate and secure the components within the structural battery pack. This foam serves as both an insulator and a structural element, providing rigidity and protection. The foam ensures that the battery cells and other critical components remain securely in place and acts as a firewall between different sections of the battery pack.
This foam is as strong as a brick, contributing to the overall structural integrity of the pack.
The video below shows a detailed analysis of the pack by Munro & Associates.
Energy Density at the Battery Pack Level
The following table shows how pack density has varied over time between some example battery packs.
| Pack | Year | Gross Capacity | Weight | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Roadster | 2010 | 53kWh | 450kg | 118 Wh/kg |
| Tesla Model S | 2012 | 85kWh | 540kg | 157 Wh/kg |
| Tesla Model X | 2015 | 75kWh | 530kg | 141 Wh/kg |
| Audi e-tron 55 | 2018 | 95kWh | 699kg | 136 Wh/kg |
| Volkswagen MEB | 2021 | 82kWh | 493kg | 166 Wh/kg |
| Tesla Model 3 LFP | 2021 | 60kWh | 477kg | 126 Wh/kg |
| Tesla Model S | 2022 | 100kWh | 544kg | 184 Wh/kg |
| Audi Q8 e-tron 55 | 2022 | 114kWh | 727kg | 157 Wh/kg |
| Kia EV6 | 2022 | 77.4kWh | 477kg | 162 Wh/kg |
| Mercedes EQXX | 2022 | 107.8kWh | 495kg | 217 Wh/kg |
| BYD Seal LR (LFP) | 2022 | 82.56kWh | 558kg | 148 Wh/kg |
| Nio Semi-Solid | 2023 | 150kWh | 575kg | 260 Wh/kg |
| Audi Q6 e-tron / Porsche Macan EV | 2024 | 100kWh | 570kg | 175 Wh/kg |
For more details about battery packs, we recommend visiting BatteryDesign.net.