DC Fast Charging
DC Fast Charging is the fastest and most convenient way of charging an EV on the road.
Last modified: Dec 31, 2024DC Fast Charging uses high-power direct current (DC) to deliver up to 1000 volts and 650 amps. This high-speed charging can add up to 200 miles of range in just 10 to 30 minutes, making it ideal for long-distance driving.
DC Fast Charging Availability
The availability of DC fast charging varies significantly depending on your location and the type of EV you drive. Some areas have numerous chargers, making it easy to find a station, while others have sparse coverage, requiring careful route planning.
Availability also varies by brand. For example, Tesla has an extensive Supercharger network, while finding a CHAdeMO plug for a Nissan Leaf can be challenging.
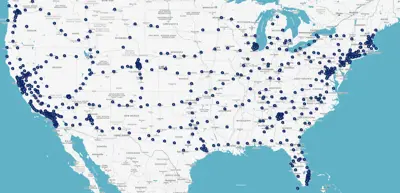
Below is a map showing the charger locations for Electrify America, highlighting areas with dense coverage and those with fewer chargers.
DC Fast Charging Performance
Charging speed can vary widely between EV models, charging stations, and even individual charging sessions. Two primary factors influence this variability:
Battery Temperature
Battery temperature is crucial for charging speed. The optimal temperature range is typically 25-35 degrees Celsius. If the battery is too cold, the Battery Management System (BMS) will reduce the charging speed to protect the battery, potentially lowering the rate to 25% of the optimal speed.
Many EVs now include battery heating systems that can be activated when navigating to a charger or manually triggered.
Charging Curve
The charging curve describes how fast an EV can charge at different states of charge (SoC). This curve is usually not flat, meaning the charging speed at 10% SoC differs from that at 80% SoC.
Charging curves vary significantly between models. Some EVs maintain a high charging speed up to 80% SoC, while others experience a steep drop-off. Maximum speeds can range from below 100 kW to over 300 kW.
Below is the charging curve for the Lucid Air Dream Edition Performance. Note the steep decline in charging speed as the SoC increases. Charging from 50% to 80% takes 20 minutes, while charging from 5% to 35% takes only 9 minutes.

To minimize charging time, identify the optimal charging range for your EV. EVKX.net provides detailed charging performance information for various models, including charging curves and optimal charging stops.
Route Planning with Charging
Most EVs offer route planning features that include DC fast charging stops to reach your destination. This functionality is part of the navigation system.
Typically, you can see the expected arrival charge level at charging stations and how much you need to charge to reach the next station.
Plug & Charge
One of the main challenges EV drivers face is the convenience and security of charging. Currently, most EV drivers need an RFID card, an app, or a contactless payment method to initiate a charging session at a public station. This can be cumbersome, especially with multiple charging networks requiring different payment systems.
Plug and charge, a feature of the international standard ISO 15118, simplifies this process. With plug and charge, drivers can plug their vehicles into a compatible station, and the session will start automatically without additional steps.
How Does Plug and Charge Work?
Plug and charge use cryptographic certificates to identify and authenticate the EV and charging station. These certificates are issued by trusted authorities and stored in secure hardware modules inside the EV and station. When an EV is plugged into a compatible station, they exchange certificates and establish a secure communication link. The station then verifies the EV’s identity and authorizes the session based on the EV’s contract with its mobility service provider (MSP).
This process ensures confidentiality, data integrity, and authenticity. It also enables dynamic tariffing, load balancing, smart grid integration, and remote firmware updates. Plug and charge can be used for AC, DC, and wireless charging.
Hubject manages the certificates based on this protocol.
Major Charging Networks by Location
USA
Several major charging networks operate in the US. According to the US Department of Energy, Tesla has over 1,600 Supercharger stations with more than 17,000 fast-charging ports. Electrify America follows with about 800 stations.
Some of the largest EV charging networks in the US include:
- Electrify America: The largest DC fast charging network for most EV models, open to all EVs with a CCS connection and some CHAdeMO vehicles like the Nissan Leaf.
Tesla Superchargers: Tesla's network is the largest in the country, with closer station spacing compared to Electrify America. Most Superchargers require a NACS port, but Tesla is adding chargers with Magic Dock to support CCS1 EVs. See chargers here.
EVgo: EVgo has over 800 fast charging locations across 34 states and more than 65 metropolitan areas.
ChargePoint: ChargePoint has over 115,000 charging spots across North America and Europe.
Europe
Several major charging networks operate in Europe. Some of the largest include:
Ionity: A high-power charging station network for EVs, enabling long-distance travel across Europe. Founded as a joint venture by BMW Group, Mercedes-Benz Group, Ford Motor Company, and Volkswagen Group.
Plugsurfing: A European-wide network that offers access to over 200,000 chargers, including those from Allego, EnBW, Eon, Innogy, IONITY, and Vattenfall, using a key or card and a free smartphone app.
Maingau: Through its EinfachStromLaden app, charging chip, or card, Maingau provides access to 50,000 charging points in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.