Home Charging
Home charging is the most convenient and cost-effective way of charging an EV.
It allows you to charge your EV overnight or whenever you are not using it without worrying about finding a public charging station.
Home charging can also reduce the grid’s stress by using off-peak electricity.
However, home charging also has some challenges. For example, not all homes have a dedicated parking space or a suitable electrical outlet for charging an EV.
How to select your charging station?
When selecting which charging station to install at your home, there are several aspects you need to consider.
First, you should understand that some limitations in your home prevent installing the charging stations you want. These limitations can be limited capacity in your area or your home that prevents installation of a powerful enough dedicated wiring/circuit. A certified electrician can help you with this.
Plugged or hardwired charging station?
The next question is to install a hardwired or plugged home charger. EVKX always recommends installing hardwired solutions. A plug/socket like Nema 14-50 has a substantial risk of overheating and causing a fire that causes harm to buildings and people.
Not recommended! Plugged charging station
Many EVs include a portable EVSE when no other charging solutions are available. You can compare it to a gas can. The best thing is to keep this EVSE in your car when you don’t have other options. In some countries, using a plugged EVSE as a permanent charging solution for your EV is prohibited.
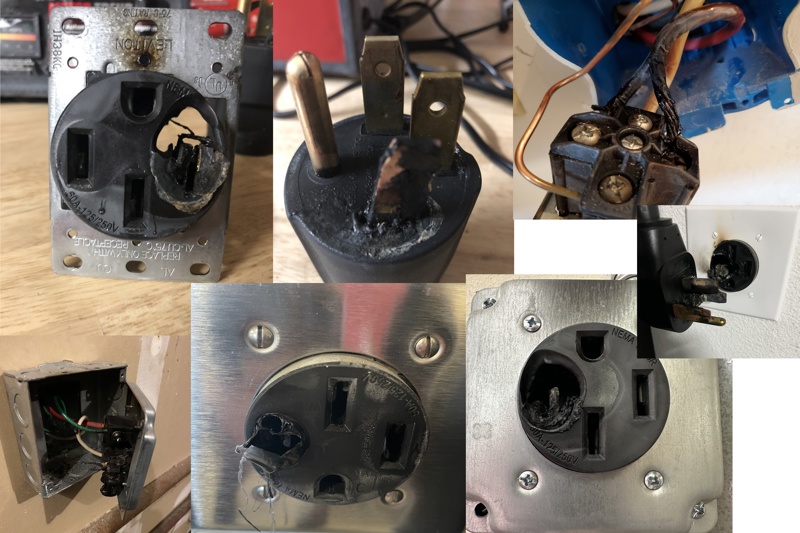
Below you see examples where people experienced overheating in plugs. Luckily, in this example, people could stop it, and no one got harmed.
Examples from owners that experienced overheated plugged solutions
If you don’t have any options other than using a plugged solution, please use high-quality plugs and try to reduce the number of times you unplug the charger. It is often the unplugging that causes wear on the plug that, again, increases the risk of overheating.
What charging capacity do you need?
So what is the capacity needed for a home charging station? This capacity depends on many factors.
What is your daily driving distance? The longer you drive each day, the more energy the charging station needs to charge the battery during the night.
How efficient is your EV? If you have a more efficient EV, that would require the charger to charge less to replenish the used energy.
The table below shows examples of energy consumed by different EVS for three daily driving distances at 120km/h / 75mph.
| Model | 50km / 31 miles | 100km / 62 miles | 200km / 124 miles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model 3 | 8.5kWh | 17kWh | 36kWh |
| Kia EV6 | 10kWh | 20kWh | 40kWh |
| Audi Q8 e-tron | 13kWh | 26kWh | 52kWh |
| Rivian R1S | 15kWh | 30kWh | 60kWh |
The table shows that Rivian R1S needs almost double the amount of energy compared to a Tesla Model 3 for the same daily driving distance.
The table below shows how much energy different chargers charge for 10 hours.
| Volt | Circuit(max load) | Capacity | 10 hour charging |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120 volt | 15(12) | 1.4KW | 14kWh |
| 240 | 15(12) | 2.8 KW | 28 kWh |
| 240 | 20(16) | 3.7 KW | 37 kWh |
| 230 | 16 | 3.7 KW | 37 kWh |
| 240 | 30(24) | 5.7KW | 57 kWh |
| 230 | 32 | 7.4 KW | 72 kWh |
| 240 | 40(32) | 7.6KW | 76 kWh |
| 240 | 50 | 9.6KW | 96 kWh |
| 400 3 phase | 16 | 11 KW | 11 kWh |
| 240 | 60(48) | 11.5KW | 115 kWh |
| 240 | 100(80) | 19.2KW | 192 kWh |
| 400 3 phase | 32 | 22 KW | 220 kWh |
As you can see from comparing the tables, even for the models with high consumption that during a 10-hour charge, you would be able to refill the energy with no problem for the example driving distances.
It would be best to consider the future when installing a new dedicated circuit. The future is Electric, and your new EV is probably not the last. So if you need a less powerful full charger now, you can still install a circuit that could handle more power in the future.
Porsche 19.2 KW hardwired charger
Check the electrical requirements of your chosen charger and compare them with your home’s existing wiring and circuit breaker. You may need to upgrade your electrical panel or install a new dedicated circuit for your charger. Hire a licensed electrician to install your home charger according to the local codes and regulations.
You may also need to obtain permits and inspections from your utility company or municipality before or after the installation.
Smart or dumb charger?
Home charging is generally cheaper and more efficient than public charging, but the exact cost and efficiency may vary depending on several factors.
Electricity rates may vary by region, season, and time of day. For example, you may pay more for electricity during peak hours (usually in the afternoon or evening) than off-peak hours (usually at night or early morning), or you may be charged for the peak level you pull from the grid.
Smart chargers let you charge when it is cheapest. Connected to the Internet, it can download prices to optimize daily charging.
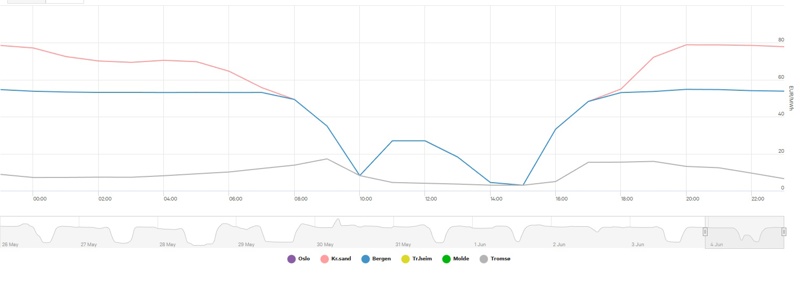
The chart below shows the next-day energy prices from Nordpool. A smart charger could use this data to plan when to charge the next day. On a sunny day like this, the energy is almost free in the middle of the day because of excess solar power. Smart charging can save a lot of money in situations like this.
Nordpool daily electricity cost Norway June 4. 2023
Country specific home charging info
USA
For home charging in USA there are two levels.
• Level 1 (120 volt): This is the standard household outlet that you can plug your EV into with a cord provided by the automaker. It provides about 5 miles of range per hour of charging and does not require any additional equipment or installation. This option is suitable for people who drive less than 50 miles a day or have access to public or workplace chargers..
• Level 2 (240 volt): This is a faster and more powerful option that requires a special charger and a 240V outlet, similar to the ones used for electric clothes dryers. It provides about 25 miles of range per hour of charging and may need an electrician to install the charger and outlet. This option is suitable for people who drive more miles a day or need to charge their EVs quickly at home.
There are also some safety rules and regulations that you should follow when installing and using home chargers for EVs. For example, the NEC 80% rule stipulates that for EV charging, electrical circuits should not be continuously loaded to more than 80% of their maximum rated capacity. This means that you should choose a charger that matches the capacity of your circuit breaker and outlet. For example, if you have a 40-amp circuit breaker and a 240V outlet, you should use a 32-amp charger (80% of 40 amps) or lower.
Another rule that may affect your home charging options is the US buildin codes. The changes specifically call for all new homes built in the US to be “EV ready”. Basically, the electrical infrastructure for EVs will be as common as a 240V outlet for home appliances. This means that if you are buying or building a new home in the US, you may already have access to Level 2 charging without any additional installation or cost.
If you want to get tips on charging stations for US market we recomend following the “State of Charge” youtube channel.
There is one charger in the US market that stands out. The Tesla Universal Wall Connector is currently the only charger that allows AC charging of EVs with NACS and J1772 connectors. This feature makes the charger future-proof for whatever EV you are buying next.
See this review to see why this charger is the one to select.
Below you see a review video of the best charing stations for 2023 (created before Teslla Universal Wall Connector was released)
UK
The home charger must be compliant with the Electric Vehicles (Smart Charge Points) Regulations 2021, which come into force on 30 June 2022 . These regulations ensure that the charger has smart functionality, allowing it to send and receive information, respond to signals to increase or decrease the rate or time of charging, provide demand side response services and a user interface, and meet certain security and privacy standards.
The home charger must also be compliant with the minimum technical specification for residential chargepoints, which defines the outlet configurations, power output, safety standards, accessibility and interoperability requirements for the charger. For example, the charger must have an outlet rated 230Vac ± 10% single-phase or 400Vac ± 10% three-phase, and an output between 3.5kW and 23kW.
The home charger must be installed by an accredited installer who is registered with the Office for Zero Emission Vehicles (OZEV) and follows the IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2018 + A1:2020) for electrical installation requirements. The installer must also ensure that the charger is compatible with the existing electrical supply and wiring of the property, and that it does not cause any interference or damage to other electrical equipment.
The home charger must not exceed a certain size and height limit for its exterior casing and upstand. The casing must not exceed 0.2 cubic metres in size, and the upstand must be 1.6m or less and there must be only one for each parking space.
See the below video for UK focused video on installing a home charger.
Most sold EVs globaly
Below, you find the top 10 most-sold EV models in the world. Click on the name for full info.