Battery Thermal Management
Thermal management is essential for battery performance and health.
Last modified: Dec 31, 2024The optimal operating temperature for a battery is around 20-30 degrees Celsius. For storage, the optimal temperature is even lower.
A battery pack has a thermal management system to maintain the battery in the best operating condition. This system includes both cooling and heating mechanisms.
Battery Heating
When the battery is too cold, it cannot accept or deliver the maximum current, which reduces the range, performance, maximum regenerative braking, and charging speed. This limitation occurs because the chemical reactions inside the battery slow down when the temperature drops, increasing internal resistance.
Charging a cold battery at a high rate can also damage the battery cells and shorten their lifespan.
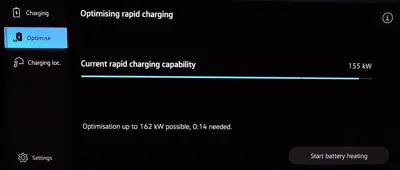
To overcome this problem, some EVs have a feature called battery preconditioning. This feature allows the EV to warm the battery to a suitable temperature before charging or driving. By doing so, the EV can preserve battery health, increase range, and shorten charging time.
How Does Battery Preconditioning Work?
Battery preconditioning uses the onboard heating system or waste heat from the motor/drivetrain to raise the battery pack’s temperature.
Automatic Preconditioning When Navigating to a DC Fast Charger
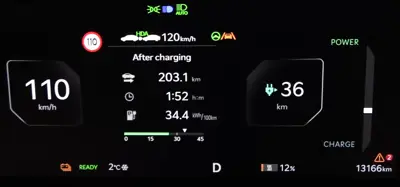
The most common way to activate battery preconditioning is to navigate to a DC Fast charger using the onboard navigation system. The system calculates, based on the distance to the charger and current temperature, how much heating is needed to reach the optimal temperature for charging. This way, the battery will be ready to accept the maximum current and charge faster.
Manually Activated Preconditioning
Some models allow manual activation of battery preconditioning. This feature enables the driver to activate heating without needing to navigate to a charger.
Preconditioning Before Traveling
If you have home charging, a good option is to precondition the battery and cabin before driving while connected to the home charger. This way, you can start with a warm cabin and battery and a fully charged battery. Typically, the driver can start preconditioning from the infotainment system or car app.
Some models do not support battery preconditioning and only precondition the cabin. For these models, it can be beneficial to ensure charging is finished just before starting the trip.
How Powerful Are the Heating Circuits?
The power of the heating circuits depends on the EV model and the battery size. For instance, the Tesla Model 3 has a 75 kWh battery pack and a 6 kW heating system, which can raise the battery temperature by about 18°C (32°F) in an hour. The Nissan Leaf has a 40 kWh battery pack and a 3 kW heating system, which can raise the battery temperature by about 9°C (16°F) in an hour.
For some models with low-power heating, getting the battery to optimal temperature in cold weather can be difficult. See the table below for some examples of battery heating power:
| Model | Heating Power |
|---|---|
| Kia Ionic 6 | 4.5 kW |
How Does Battery Preconditioning Affect the Range?
Battery preconditioning consumes some energy from the battery, which reduces the available range. However, this energy loss is partially compensated by the improved efficiency and performance of the battery at a higher temperature. Moreover, preconditioning the battery while the EV is plugged in can minimize the energy loss, as the EV can draw power from the grid instead of the battery.
Minimum SOC Level for Preconditioning
Most EVs have a limit on how low the State of Charge (SOC) can be for preconditioning to activate.
You can see in this test from Bjørn Nyland how the Kia EV9 disables preconditioning at 12% SOC.
Battery Cooling
The battery temperature can rise to high levels during high-speed charging or sporty driving. When the battery is too hot, it can degrade faster, lose capacity, and reduce the range. This effect occurs because the chemical reactions inside the battery accelerate when the temperature rises, and the internal resistance decreases. Charging a hot battery at a high rate can also damage the cells and shorten their lifespan.
Typically, manufacturers will derate both charging and power output if the battery temperature is too high.
To overcome this problem, some EVs have active battery cooling. This feature allows the EV to lower the battery's temperature to a suitable level during charging or driving to increase charging or driving performance.
How Does Battery Cooling Work?
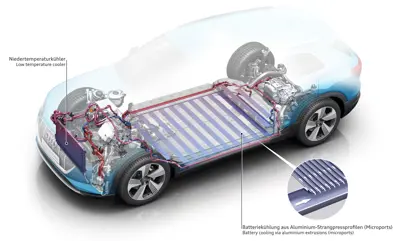
Battery cooling uses a liquid-based system that circulates a coolant through the battery pack. The coolant absorbs the heat from the battery cells and transfers it to a radiator. The radiator then dissipates the heat to the ambient air or another cooling loop using a refrigerant or heat pump. The coolant can be a water-ethylene glycol mixture, a dielectric fluid, or a fluid containing thermally conductive particles.
In this 1000km test by Bjørn Nyland, the BMW i50 has a problem with overheating after charging and reduced available power.