Suspension
The suspension is one of the essential parts of an EV drivetrain. Again, EVKX.net gives you all details.
What is the purpose of suspension?
The suspension system in cars is designed to provide a smooth and comfortable ride for passengers while ensuring vehicle stability, control, and safety. It serves several vital functions:
- Maintaining tire contact with the road surface: Ensures traction, steering, and braking by keeping the wheels in contact with the road.
- Absorbing shock and vibration: Minimizes the impact of bumps and rough roads on the vehicle and its passengers.
- Supporting the vehicle's weight: Supports the chassis, engine, passengers, and cargo.
- Providing stability and control: Maintains stability and control during cornering, braking, and acceleration.
- Enhancing handling and performance: Improves handling and performance, allowing the vehicle to navigate corners and obstacles with ease.
Overall, the suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring the vehicle's comfort, safety, and performance.
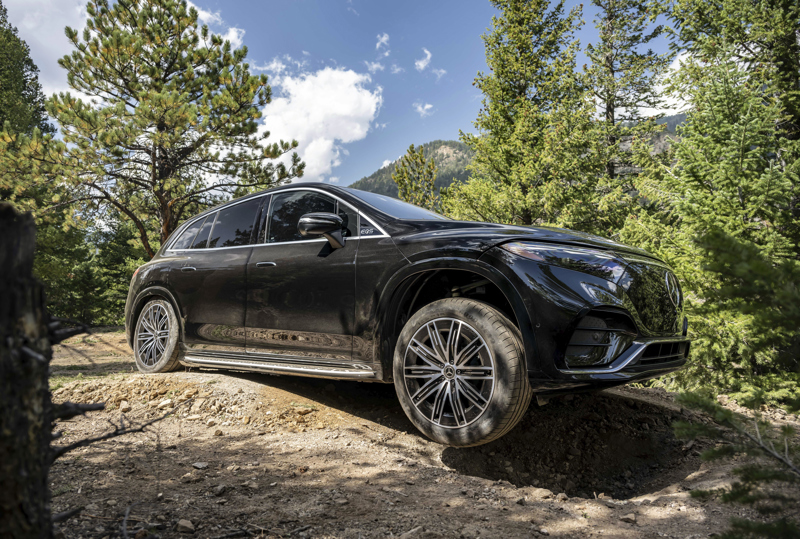
Mercedes EQS SUV Offroad
What are the parts of a suspension system?
The main components of a car's suspension system typically include:
- Springs: Absorb and store energy when the suspension compresses and release it when it rebounds. Made of steel coils, air bags, or other materials.
- Shock absorbers or dampers: Reduce oscillations caused by the springs by dissipating energy. Help maintain tire contact with the road by controlling spring rebound and compression.
- Control arms: Connect the wheel hub assembly to the vehicle's chassis or subframe, controlling wheel movement while allowing some lateral and longitudinal movement.
- Sway bar or stabilizer bar: Minimizes body roll and improves stability during cornering by connecting the left and right wheels.
- Struts: Similar to shock absorbers but also support the vehicle's weight. Commonly used in MacPherson strut suspension systems.
- Bushings: Small rubber or polyurethane components that isolate and dampen vibrations and noise between different suspension components.
The suspension system is a complex assembly of components that work together to provide a smooth and comfortable ride while maintaining stability, control, and safety.
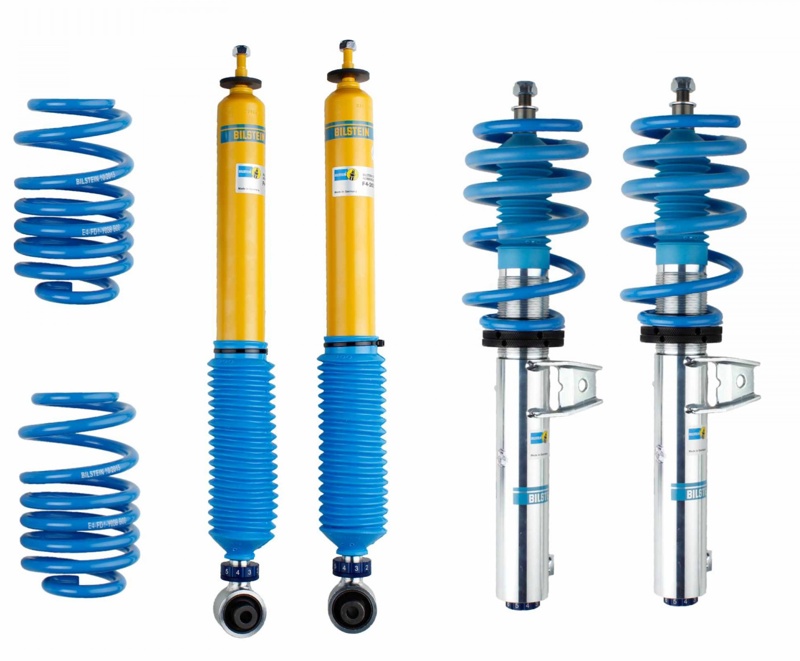
Bilstein dampers and springs
Suspension Types
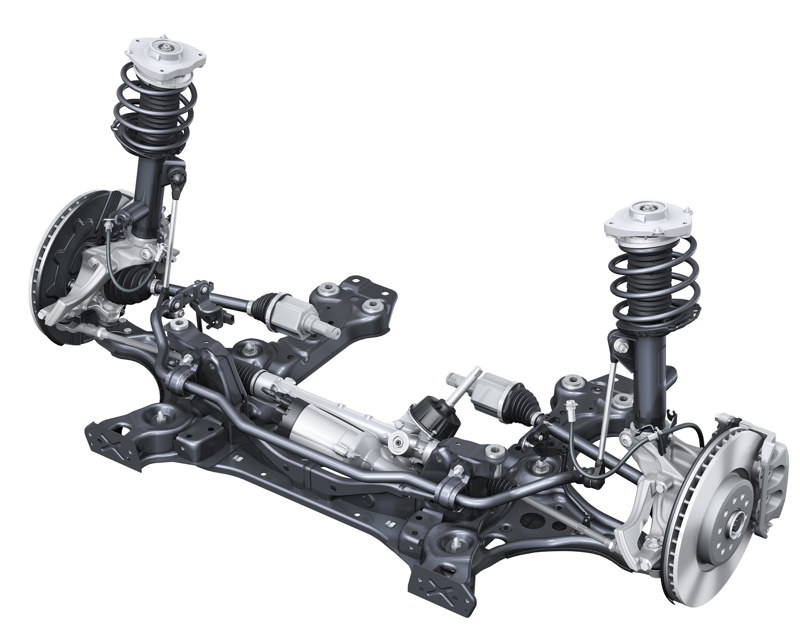
MacPherson Strut
The MacPherson strut is an automotive suspension system that uses the top of a telescopic damper as the upper steering pivot. It is commonly used as the front suspension in medium to low-priced EVs. Named after engineer Earle S. MacPherson, who developed the design, it uses a wishbone or a substantial compression link stabilized by a secondary link, providing a mounting point for the hub carrier or axle of the wheel.
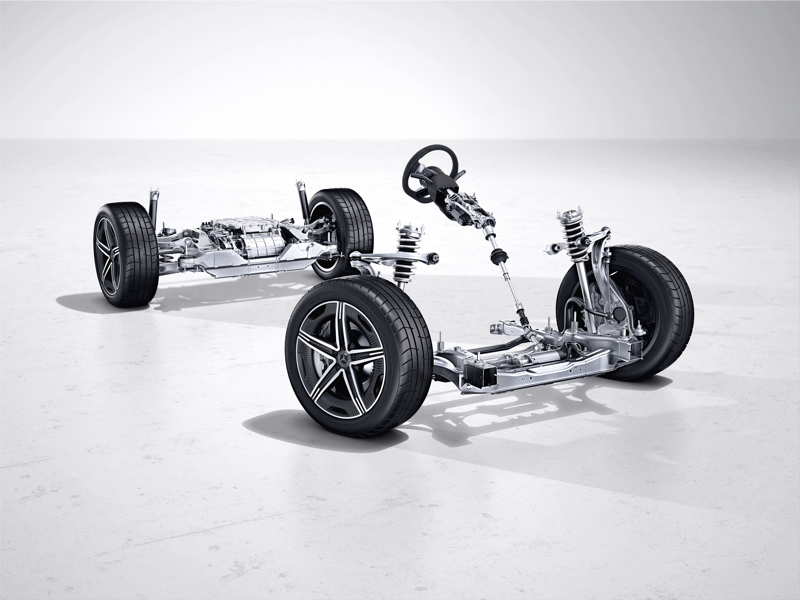
McPherson front suspension Audi Q4
Pros of MacPherson Strut
- Simplified design: Fewer components make it easier to install and maintain.
- Space-efficient: Takes up less space, leaving more room for other components.
- Good handling: Provides good handling and stability, especially in high-speed maneuvers and cornering.
- Cost-effective: Generally less expensive than other suspension systems.
Cons of MacPherson Strut
- Limited adjustability: Less adjustable, making it harder to fine-tune ride and handling characteristics.
- Less durable: May be less durable in harsh driving conditions or off-road use.
- Bump steer: Can cause wheels to steer unintentionally during cornering.
- Uneven tire wear: Can cause uneven tire wear, especially on rough roads or bumps.
Double Wishbone
Double wishbone suspension is a type of independent suspension system commonly used in high-performance and luxury vehicles. It features two A-shaped control arms (wishbones) connected to the chassis and the wheel hub assembly, allowing for precise control of wheel movement.
Mercedes-Benz EQE Suspension with double wishbone
Pros of Double Wishbone
- Improved handling: Allows for better handling, steering response, and stability.
- Better ride quality: Reduces the impact of bumps and road imperfections.
- Good camber control: Maintains tire contact with the road during hard cornering.
- Highly adjustable: Allows for fine-tuning of handling characteristics, ride height, and suspension geometry.
Cons of Double Wishbone
- Complex design: More complex and expensive to design, manufacture, and maintain.
- Space requirements: Takes up more space, limiting vehicle design and packaging options.
- Heavy: Can be heavier, affecting vehicle weight and fuel economy.
- Cost: More expensive to repair or replace.
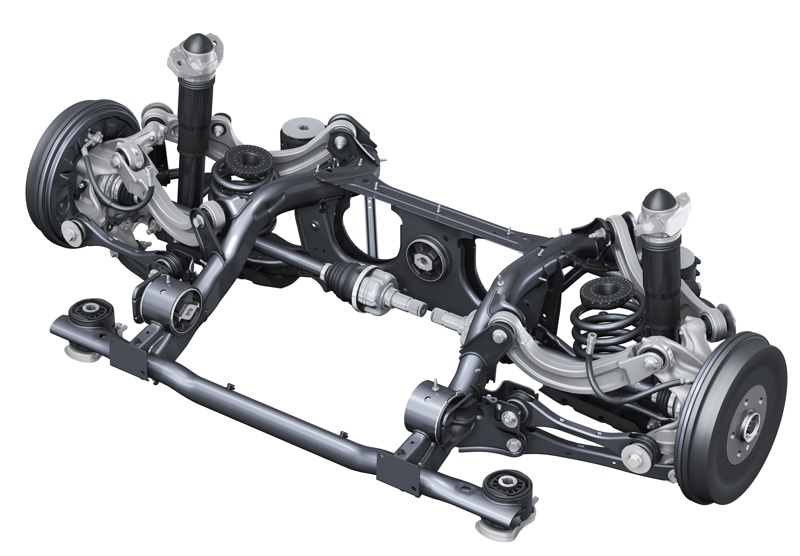
Multilink
Multilink suspension is an independent suspension system designed to provide superior ride comfort and handling performance. It consists of multiple links connecting the wheel hub to the vehicle's chassis, allowing each wheel to move independently.
Multilink rear suspension
Pros of Multilink Suspension
- Improved handling: Provides better handling and stability, especially at high speeds.
- Better ride comfort: Absorbs bumps and shocks more effectively.
- Versatile design: Suitable for a wide range of vehicle types and sizes.
Cons of Multilink Suspension
- Complex design: More difficult and expensive to repair or maintain.
- High manufacturing costs: Increases the price of the vehicle.
- Heavy weight: Adds significant weight, affecting fuel efficiency and performance.
- Requires more space: Limits available interior space or complicates packaging of other components.
Leaf Suspension
Leaf suspension uses a series of curved metal plates called leaf springs, mounted on the vehicle's frame and axles. It provides a smooth ride and supports the vehicle's weight.
Pros of Leaf Suspension
- High weight capacity: Ideal for heavy-duty trucks and trailers.
- Simple design: Less expensive to manufacture and repair.
- Good durability: Can withstand heavy loads and rough terrain.
Cons of Leaf Suspension
- Stiff ride: Can be uncomfortable for passengers.
- Limited adjustability: Difficult to fine-tune for optimal performance.
- Poor handling: Can cause bouncing and swaying on rough roads.
- Noise and vibration: Can produce noise and vibration when driving.
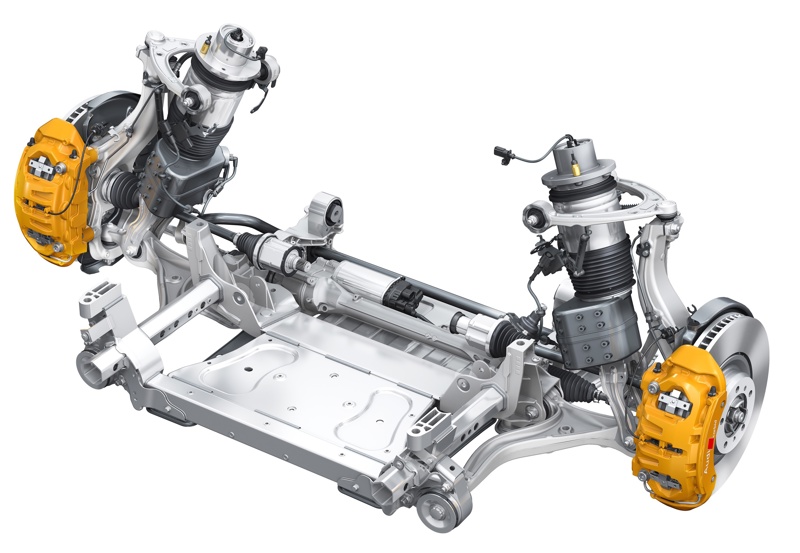
Air Suspension
Air suspension uses compressed air to provide support and cushioning. It consists of airbags, a compressor, and a control system that adjusts the height and stiffness of the suspension.
Pros of Air Suspension
- Comfortable ride: Provides a smoother ride than traditional systems.
- Adjustable: Accommodates different loads and road conditions.
- Improved handling: Lowers the vehicle's center of gravity, enhancing stability.
- Reduces wear and tear: Minimizes wear on tires and suspension components.
Cons of Air Suspension
- Expensive: More costly to repair or replace.
- Complex: More components that can fail or malfunction.
- Energy consumption: Compressor can reduce fuel efficiency.
Some models use air suspension only to adjust for different loads, maintaining a consistent ride height. Others allow the driver to set the ride height based on drive mode.
Front Air Suspension
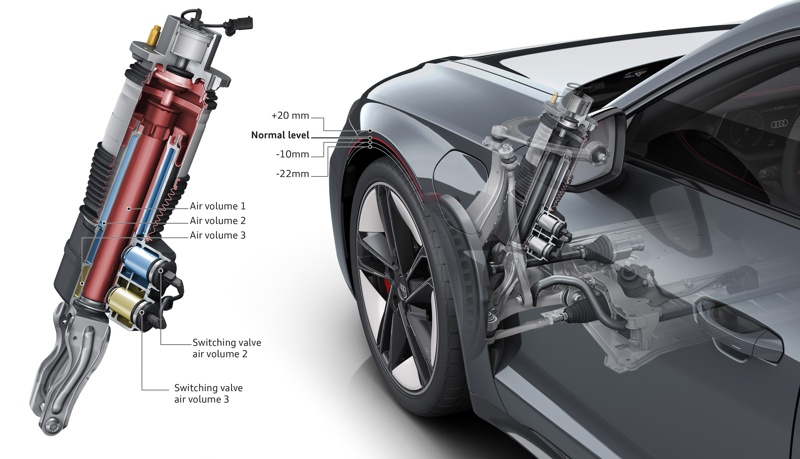
Adaptive Damping
Adaptive damping suspension adjusts the damping of a car's suspension system in real-time based on driving conditions and driver preferences. Sensors detect the car's motion, and a computer adjusts the damping accordingly.
Pros of Adaptive Damping
- Improved comfort: Provides a smoother ride.
- Better handling: Enhances handling and stability on uneven roads.
- Customizable: Can be tailored to the driver's preferences.
Audi RS e-tron GT adaptive air suspension